Important organic chemical FUNCTIONAL
GROUPS found in biological molecules (R = any organic group)
This page is for reference. Learn these only as they are discussed in class.
They should be memorized so we can talk about them easily.
|
NAME |
GROUP |
CHEMICAL EXAMPLE |
COMMENT |
BIOLOGICAL EXAMPLE |
|||||
|
hydroxyl: |
-OH |
ethanol: CH3-CH2-OH |
polar |
sugars
(e.g., fructose) |
|||||
|
aldehyde: |
-CHO |
acetaldehyde: CH3-CHO |
polar |
glucose |
|||||
|
detail: |
O |
|
|
|
|||||
|
carboxylic
acid: |
-COOH |
acetic
acid: CH3-COOH |
charged |
fatty acid
(e.g., oleate) |
|||||
|
detail: |
|
|
|
||||||
|
amine: |
-NH2 |
methyl
amine: CH3-NH2 |
charged |
amino acid
(e.g., glycine) |
|||||
|
detail: |
(-NH3+) |
|
|
|
|||||
|
ketone: |
-CO- |
acetone: CH3-CO-CH3 |
polar |
metabolic intermediate
|
|||||
|
detail: |
O |
|
|
|
|||||
|
ether: |
-O- |
ethyl
ether: CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH3 |
not so
polar (symmetric) |
some
lipids |
|||||
|
ester: |
-COOR |
methyl
ester of acetic acid: CH3-CO-OCH3 |
polar. not
charged |
fats (e.g.,
triglycerides) |
|||||
|
detail: |
O |
|
|
|
|||||
|
amide: |
-CONH2 |
acetamide: CH3-CONH2 |
polar, not
charged |
proteins
(e.g., asparagine) |
|||||
|
detail: |
O |
|
|
|
|||||
|
sulfhydryl: |
-SH |
2-mercaptoethanol: HO-CH2-CH2-SH |
reducing
agent |
protein (cysteine) |
|||||
|
disulfide: |
-S-S- |
R-S-S-R |
crosslinks in proteins |
protein (cystine) |
|||||
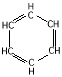
|
phenyl: |
|
phenol: C6H5-OH,
Ø-OH |
hydrophobic |
proteins
(phenylalanine) |
|||||
|
anhydride |
O O- |
3-phosphogyceric
acid: HOCH-CHOH-CO-O-P03-- |
2 acids
joined |
intermediary
metabolites |
|||||
|
guanidino |
-N-C-NH2 |
arginine: +H3N-CH-CH2-CH2-CH2-NH-C-NH2 |
charged |
proteins
(arginine) |
|||||