Bīrūnī, Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad, Alberuni's India (v. 1)
(London : Kegan Paul, Trench, Trübner & Co., 1910.)
|
||
|
|
|
|
| Page 235 |
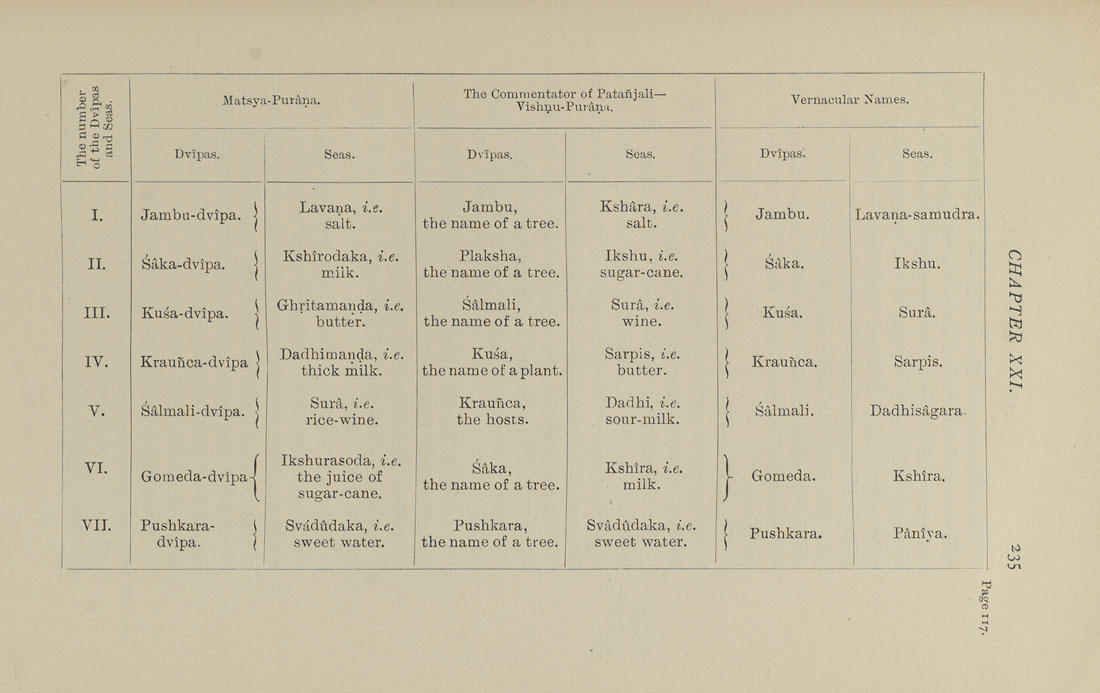
The number
of the Dvipas
and Seas.
Matsya- Purana.
The Commentator of Patanjali—
Vish^u-Purana.
Vernacular Names.
Dvipas.
Seas.
Dvipas.
Seas.
Dvipas.
Seas.
Lavana-samudra.
Ikshu.
Sura.
Sarpis.
Dadhisagara.
Kshira.
P&niya.
I.
II.
III.
IV.
V.
VI.
VII.
Jamb a-dvipa. j
Saka-dvipa. j
Kusa-dvipa. ]
Kraunca-dvipa j
SMmali-dvipa. -j
Gomeda-dvipa-j
Pushkara- {
dvipa. (
Lavana, i.e.
salt.
Kshirodaka, i.e.
milk.
Ghritamanda, i.e.
butter.
Dadhimaiicla, i.e.
thick milk.
Sura, i.e.
rice-wine.
Ikshurasoda, i.e.
the juice of
sugar-cane.
Svadtidaka, i.e.
sweet water.
Jambu,
the name of a tree.
Plaksha,
the name of a tree.
Salmali,
the name of a tree.
Kusa,
the name of a plant.
Kraunca,
the hosts.
Saka,
the name of a tree.
Pushkara,
the name of a tree.
Kshara, i.e.
salt.
Ikshu, i.e.
sugar-cane.
Surfl, i.e.
wine.
Sarpis, i.e.
butter.
Dadhi, i.e.
sour-milk.
Kshlra, i.e.
milk.
Svadudaka, i.e.
sweet water.
( Jambu.
1 Saka.
[ Kusa.
[ Kraunca.
1 Salmali.
]
Y Gomeda.
[ Pushkara.
|
| Page 235 |