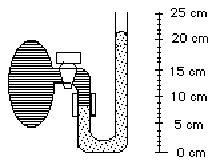
1. There is a gas trapped in the egg-shaped bulb (on the left in the following sketch) by the mercury in a manometer. What is the pressure of the gas if atmospheric pressure is 1.00 atm?
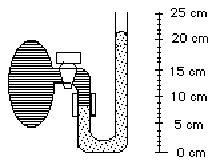
(1) 0.17 atm (2) 0.83 atm (3) 1.00 atm (4) 1.17 atm (5) 2.00 atm
2. A glass bulb of volume V contains 0.440 g of CO2 at STP. This bulb is evacuated and filled with an unknown gas. If the unknown gas filling the volume V weighs 0.280 g at STP, what is the molecular weight of the unknown gas?
(1) 63.6 g/mol (2) 44.0 g/mol (3) 28.0 g/mol (4) 22.4 g/mol (5) 14.0 g/mol
3. Which of the statements concerning the graphs that follow are consistent with the ideal gas law for one mole of gas?
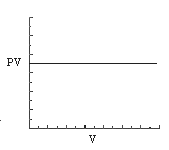
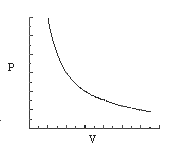 graph B
graph B
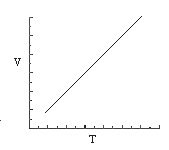
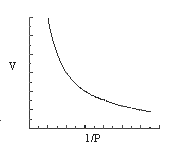 graph D
graph D
(1) only graph B is a reasonable representation.
(2) only graphs A and C are reasonable representations.
(3) only graphs B and D are reasonable representations.
(4) only graphs A, B, and C are reasonable representations.
(5) all four graphs are reasonable representations.
4. If the average speed of chlorine molecules at 298K and 1.0 atm is 3.24 X 104 cm/s, then the average speed at 298 K and 2.0 atm is.....
(1) 6.48 X 104 cm/s (2) 3.24 X 104 cm/s (3) 1.62 X 104 cm/s (4) 0.81 X 104 cm/s (5) sqrt(3.24 X 104) cm/s
5. The valve between a 5.0 L tank in which the gas pressure is 6.0 atm and a 10. L tank in which the pressure is 9.0 atm is opened. Assuming the connecting tube is zero volume and constant temperature, the equilibrium final pressure is...........
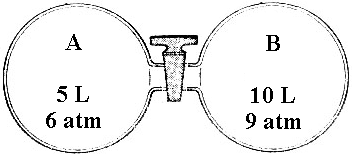
(1) 3.0 atm (2) 7.0 atm (3) 7.5 atm (4) 8.0 atm (5) 15 atm
6. An ideal mixture is prepared by mixing 4 moles of O2 with 8 moles of H2. The mixture is allowed to effuse through a pin hole. What is the mole fraction of O2 in the effused mixture?
(1) 2/9 (2) 2/3 (3) 8/9 (4) 1/9 (5) 4/5
7. The moon has no atmosphere whereas the earth has an atmosphere. It follows from the kinetic theory of gases that the earth presumably is losing lower molecular weight atmospheric gases faster than higher molecular weight gases, and that eventually earth, too, will lose its atmosphere altogether. Which of the following features of kinetic theory dictates that conclusion?
(1) The mean speed increases with sqrt(T/M).
(2) The mean kinetic energy per particle is 3kT/2.
(3) The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution of speeds.
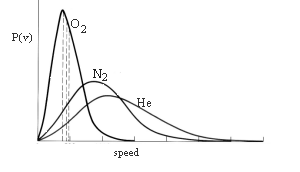
(4) The kinetic theory can be used to deduce the ideal gas equation of state.
8. The following table contains values for the van der Waals constants a and b for two gases X and Y:
| a(atm L2mol-2) | b(L mol-1) |
|---|---|
| 1.36 | 0.0318 |
| 6.71 | 0.0564 |
From the information in the table, it can be concluded that X molecules are.....
(1) larger and more attracted to one another compared to Y molecules.
(2) larger and less attracted to one another compared to Y molecules.
(3) smaller and more attracted to one another compared to Y molecules.
(4) smaller and less attracted to one another compared to Y molecules.
THE NEXT THREE QUESTIONS ARE BASED ON THE DATA SUPPLIED IN THE FOLLOWING PHASE DIAGRAM FOR WATER. Note that the pressure and temperature scales are not continuous - the scales change. Note also Tc = 374°C and Pc = 218 atm.
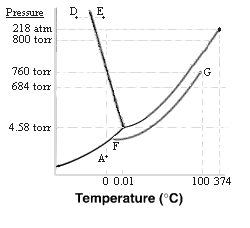
9. The phase changes occurring from point A to 800 torr upon compression of H2O at constant temperature are progressively ....
(1) solid to liquid to gas
(2) gas to liquid to solid
(3) gas to solid to liquid
(4) solid to liquid to solid
(5) liquid to solid to gas
10. The phase changes occurring on heating from point D to point E at constant pressure are progressively...
(1) liquid to gas
(2) solid to liquid
(3) solid to gas
(4) liquid to solid
(5) gas to liquid
11. Consider the ideal solution suggested by the segment FG (in the diagram on the preceding page). Determine the number of moles of water present for each mole of solute:
(1) 1:1 (2) 1:9 (3) 9:1 (4) 9:10 (5) 10:9
12. The critical conditions for ammonia and chlorine are, respectively, 132°C and 112 atm, and 144°C and 76 atm. At 144°C and 76 atm....
(1) only chlorine can be liquified.
(2) only ammonia can be liquified.
(3) chlorine and ammonia can both be liquified.
(4) neither chlorine nor ammonia can be liquified.
13. Assuming ideal behavior, what is the vapor pressure of a solution of 16.0 mol of chloroform and 4.00 mol of dioxane at 23 °C?
Vapor Pressures at 23 °C(1) 50.4 torr (2) 62.8 torr (3) 74.2 torr (4) 87.6 torr (5) 138. torr
14. Actually, chloroform and dioxane (in the above example) do not form an ideal solution since chloroform hydrogen bonds to electronegative oxygen atoms in dioxane molecules. The result of that interaction is....
(1) positive deviation from ideal behavior and heat is evolved on solution.
(2) positive deviation from ideal behavior and heat is absorbed on solution.
(3) negative deviation from ideal behavior and heat is evolved on solution.
(4) negative deviation from ideal behavior and heat is absorbed on solution.
15. Which of the equations below can be used to calculate the molality m of a solution (where g represents weight in grams of indicated species, M refers tothe molecular weight of the species, and the subscripts 1 and 2 refer to solvent and solute, respectively:
(1) (g2 1000) / (M2g1)
(2) (n2 1000) / g1
(3) (n2 1000) / (n1M1)
(4) all of the above
(5) none of the above
16. Polyvinyl chloride is a polymer used in applications as diverse as outdoor plumbing and shower curtains. When 4.0 g of a polyvinvyl chloride was dissolved in 1 L of dioxane, the osmotic pressure at 25°C was measured to be 0.494 torr. Therefore the molecular weight of the polymer must be.....
(1) 2.65 X 10-5 g/mol
(2) 4.53 X 101 g/mol
(3) 1.81 X 102 g/mol
(4) 1.98 X 102 g/mol
(5) 1.50 X 105 g/mol
17. Which water solution has the lowest freezing point?
(1) 0.1 m Na2SO4
(2) 0.1 m NaCl
(3) 0.1 m KNO3
(4) 0.1 m C12H22O11 (sugar)
(5) 0.1 m HC2H3O2
18. For the following reaction, indicate whether the equilibrium constant K (increases, decreases, stays the same) with increasing temperature, for the following reaction. Note that Û is used here in place of the usual double, half-headed arrows indicating equilibrium:
N2O4 (colorless gas) Û 2 NO2 (red gas)
(1) increases (2) stays the same (3) decreases
19. Using the equilibrium constants given for reactions (1) and (2), the equilibrium constant for reaction (3) is...
(1) N2O4(g) = 2NO(g) + O2(g) Kp(1) = 6.71x10-14
(2) 2NO(g) + O2(g) = 22 NO2(g) Kp(2) = 1.66x1012
(3) 22 NO2(g) = N2O4(g) Kp(3) = ?
(1) 0.0123 (2) 0.111 (3) 1.11 (4) 8.98 (5) 80.3
20. A violin string of length L is plucked. The wavelength of the fundamental vibration of this violin string is l = L/2. The pitch (frequency) of the sound generated by this string can be computed from the formula ln = c where c is the speed of sound in the ambient gas surrounding the string. Thus, the pitch is n = c/l = 2c/L. This would be true of a vocal cord, too. So, when Jack sang "La Donna e Mobile" (the Don's song from Verdi's Rigoletto), the pitch of his voice was higher when he inhaled helium than when he inhaled air. A likely explanation of this phenomenon is...
(1) Helium gas caused a shortening of Jack's vocal cord.
(2) The speed of sound is higher in helium than in air.
(3) Helium caused a decrease in the power of exhalation.
(4) the Doppler effect.
(5) none of the above.
21. This device, an inverted "thistle tube across which a semipermeable membrane has been stretched, can be used to measure osmotic pressure. It is initially filled with fresh water and set in a beaker containing a saturated salt solution so that the height of the liquid stands a distance h above the surface level of the surrounding solution. At equilibrium......
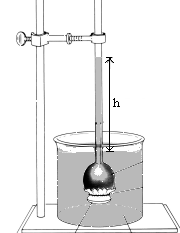
(2) h will be the same as the initial value.
(3) h will be zero.
(4) h will be less than the initial value.