At 650°C, the total pressure of the gases present is 0.80 atm and both solids are present. Kp for this reaction at the indicated temperature is.........
(1) 0.16 (2) 0.40 (3) 0.64 (4) 0.80 (5) 1.60
2. A reaction vessel is filled initially with p = 0.50 atm each of SO2, SO3, NO, and NO2. For the reaction at 1000K, Kp is equal to 1/9:
At equilibrium, p(SO3) is.......... (1) 0.111 (2) 0.250 (3) 0.500 (4) 0.750 (5) 0.900
3. The correct ordering of the relative solubilities of AgCl(s) in water and aqueous solutions of 0.1M silver nitrate and 0.1M ammonia is....
| (a) in pure water | (b) in 0.10 M AgNO3 | (c) in 0.10 M aq NH3 |
4. An unknown student takes an unknown weight of an unknown weak monoprotic acid and dissolves it in an unknown amount of water. The unknown student then divides the aqueous solution into two equal volumes, titrates one volume to a phenophthalein endpoint, and then adds the other volume to the titrated solution. The pH of the combined volumes turns out to be 4.67. The Ka of the weak acid is.... (1) 0.33 X 105 (2) 1.8 X 10-5 (3) 2.14 X 10-5 (4) 4.67 X 10-5 (5) 104.67
5. A saturated aqueous solution of CO2 is (basic, neutral, acidic) while a saturated aqueous solution of H2S is (basic, neutral, acidic): (1) basic, basic (2) basic, acidic (3) acidic, basic (4) acidic, acidic (5) neutral, neutral
6. A saturated soution of lanthanum iodate, La(IO3)3, in pure water has a concentration of iodate ion equal to 2.07 X 10-3M at 25°C. What is the solubility product of lanthanum iodate? (1) 0.69 X 10-4 (2) 2.07 X 10-4 (3) 1.43 X 10-6 (4) 1.84 X 10-11 (5) 6.12 X 10-12
7. On adding 0.100 M sulfuric acid to a barium hydroxide solution, at the equivalence point.... (1) the solution conducts, as evidenced by the glowing light bulb. (2) the solution does not conduct, as evidenced by the extinction of the light bulb (3) the solution is acidic, due to hydrolysis (4) the solution is basic, due to hydrolysis (5) the solution turns pink
8. Which of the following elements is not in its standard state?
(1) F2(g)
(2) H2(g)
(3) O3(g)
(4) Hg(liq)
(5) I2(s)
9. Which of the following processes is expected to be exothermic?
(1) freezing Hg(liq) at its normal melting point (-38.4°C)
(2) combustion of diamond to form CO2(g)
(3) cooling of 1.0 kg of water from 10.0°C to 5.00°C.
(4) all of the above are exothermic
(5) none of the above are exothermic.
10. Given the following thermochemical equations, calculate the standard enthalpy of formation for propane, C3H8(g):
(1) -3131 kJ (2) -1773 kJ (3) + 129 kJ (4) +3131 kJ (5) +4775 kJ
11. An ice cube at 0.00°C and weighing 18.0 grams is placed in 180. grams of water at 25.0°C in an isolated system. What is the temperature of the system at equilibrium, given that the heat of fusion for ice is -6,007 J/mol and the specific heat capacity for water is 4.184 J/g·K?
(1) not all the ice melts, so T = 0.00°C
(2) 5.00°C
(3) 15.6°C
(4) 17.1°C
(5) 24.0°C
12. At 60°C, the autoprotolysis constant (Kw) of water is 9.6 X 10-14. What is the pH of an aqueous solution that has an OH- concentration of 5.0 X
10-5M?
(1) 5.7
(2) 6.7
(3) 7.7
(4) 8.7
(5) 9.7
13. What effect will the addition of pure water to an aqueous solution of a base have on the pH of the basic solution?
(1) raise it
(2) lower it
(3) leave it unchanged
(4) cannot say without more information
14. What is the pH of the resulting solution when 50.0 mL of an 0.10 M HCl solution is added to 100 mL of an 0.20 M NaOH solution?
(1) 14
(2) 13
(3) 12
(4) 11
(5) 10
15. Suppose the following four salts have the same numerical values of Ksp<<1. Which salt will have the highest solubility?
(1) AB
(2) AB2
(3) AB3
(4) A2B3
16. Given that Kb(F-) = 1.5 X 10-11 at 25°C, then Ka(HF) must be.......
(1) 3.3 X 10-7
(2) 6.7 X 10-5
(3) 6.7 X 10-4
(4) 3.3 X 10-3
(5) 1.5 X 103
17. Given Kb(CN-) = 1.6 X 10-5 and Kb(F-) = 1.5 X 10-11, then the equilibrium constant for the following reaction must be........
(1) 2.4 X 10-16 (2) 4.1 X 10-12 (3) 9.4 X 10-7 (4) 1.1 X 106 (5) 4.1 X 1012
18. An 0.05 M acetic acid solution [Ka(HOAc) = 1.8 X 10-5] has a pH of......
(1) 1.7
(2) 4.8
(3) 3.0
(4) 3.4
(5) 5.0
19. An 0.10 M NaOAc solution [Ka(HOAc) = 1.8 X 10-5] has a pH of.....
(1) 5.1
(2) 7.0
(3) 7.9
(4) 8.9
(5) 10.1
20. The amino acid glycine can exist in aqueous solution in several different states - as neutral molecues (NH2CH2COOH) ; as the conjugate base (NH2CH2COO-); as the conjugate acid (+NH3CH2COOH); and as zwitter ions (+NH3CH2COO-). Given the following Ka values for the dissociations....
determine the concentration of the zwitterion (+NH3CH2COO-) in a solution prepared by dissolving 0.01 mole of glycine (NH2CH2COOH) in enough water to make a liter of solution.
Hint: In order to do that, you will first have to find the equilibrium constant for the reaction
(1) 0.01 M (2) 0.10 M (3) 0.001 M (4) 0.05 M (5) 0.5 M
21. The titration curve below describes the titration of a certain weak base with a strong acid. From the plot, estimate the pKb for the weak base in question.
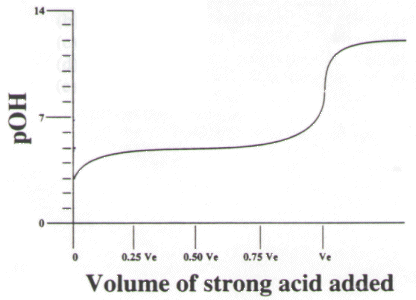 (1) 4
(2) 5
(3) 6
(4) 7
(5) 8.7
(1) 4
(2) 5
(3) 6
(4) 7
(5) 8.7
22. The pKa for formic acid is 3.74. What is the pH of the solution resulting from addition of 0.50 mole of formic acid (HCOOH) and 0.30 mole sodium formate (HCOO-) to enough water to create a final volume of 1.0 L?
(1) 2.18
(2) 2.78
(3) 4.35
(4) 3.52
(5) 1.00
23. If the above solution is diluted by the addition of 0.50 L of pure water, the pH will....
(1) decrease
(2) increase
(3) stay the same
(4) become neutral
(5) become basic
24. If 0.01 mole of NaOH crystals are added to the above solution, ignoring any volume increase in problem 22 (above) the pH will change to
(1) 2.38
(2) 2.80
(3) 4.37
(4) 3.54