SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Testis and Epididymis
#56 Testis, Human, Adult, H&E
Open with WebViewer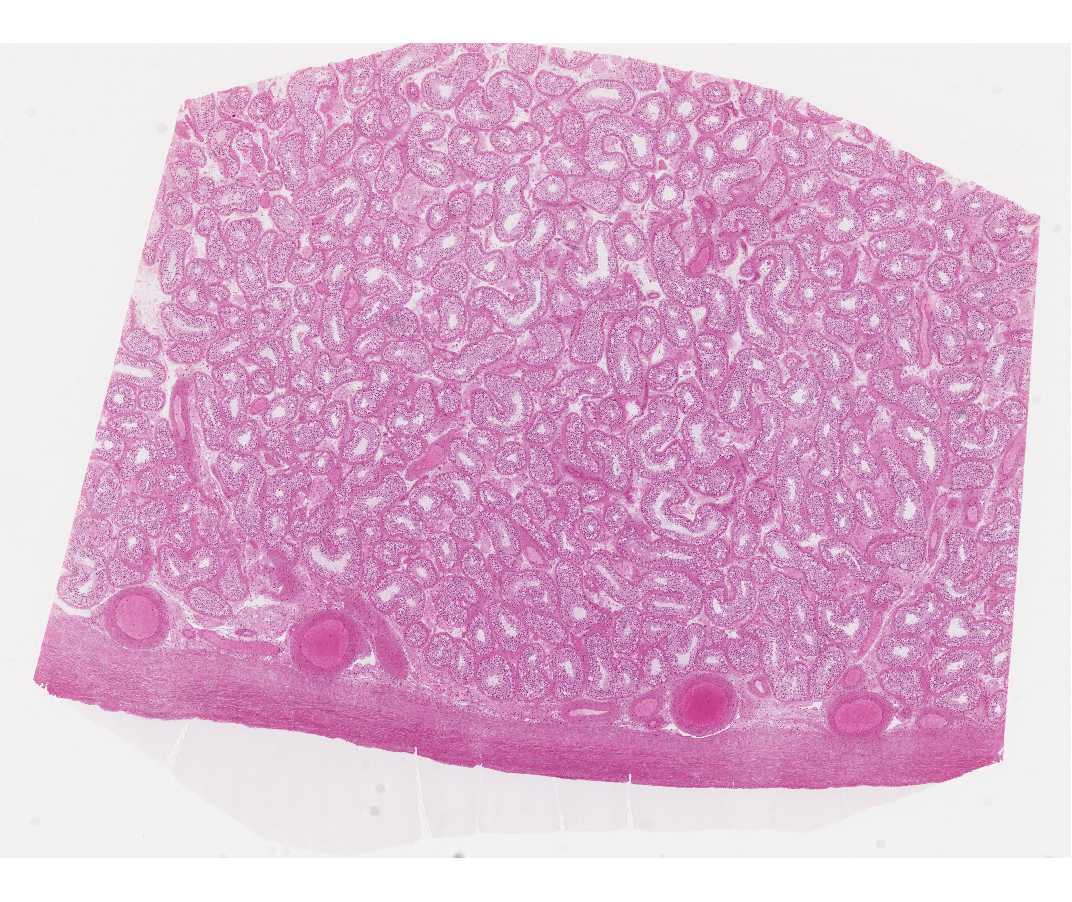
Identify with low magnification, the tunica albuginea - the fibrous capsule surrounding the testis and the testis.
At higher magnification identify the germinal elements (spermatogonia, spermatocytes and spermatids) and sustentacular (Sertoli) cells in the seminiferous tubules. Only the Sertoli cells and spermatogonia (usually with interphase nuclei) rest on the basement membrane. The larger primary spermatocytes lie on the luminal side of the Sertoli cells and are frequently in some stage of the prolonged prophase of the first meiotic division. Secondary spermatocytes rapidly undergo the second meiotic division and are therefore rarely seen. During spermiogenesis the spermatids are remodeled into streamlined motile cells, the spermatozoa. The entire process of gamete production (i.e., spermatogonia to spermatozoa) is known as spermatogenesis. The germinal elements characteristically occur in small associations of synchronized cells. Beneath the basement membrane of the tubules note the myoid cells (myoepithelium) with their pale-staining elongated nuclei.
In the interstitium (between the seminiferous tubules) identify Leydig cells, which are large eosinophilic cells. Why are they eosinophilic?
#57 Testis and Epididymis, Monkey, Rabbit, H&E
Open with WebViewer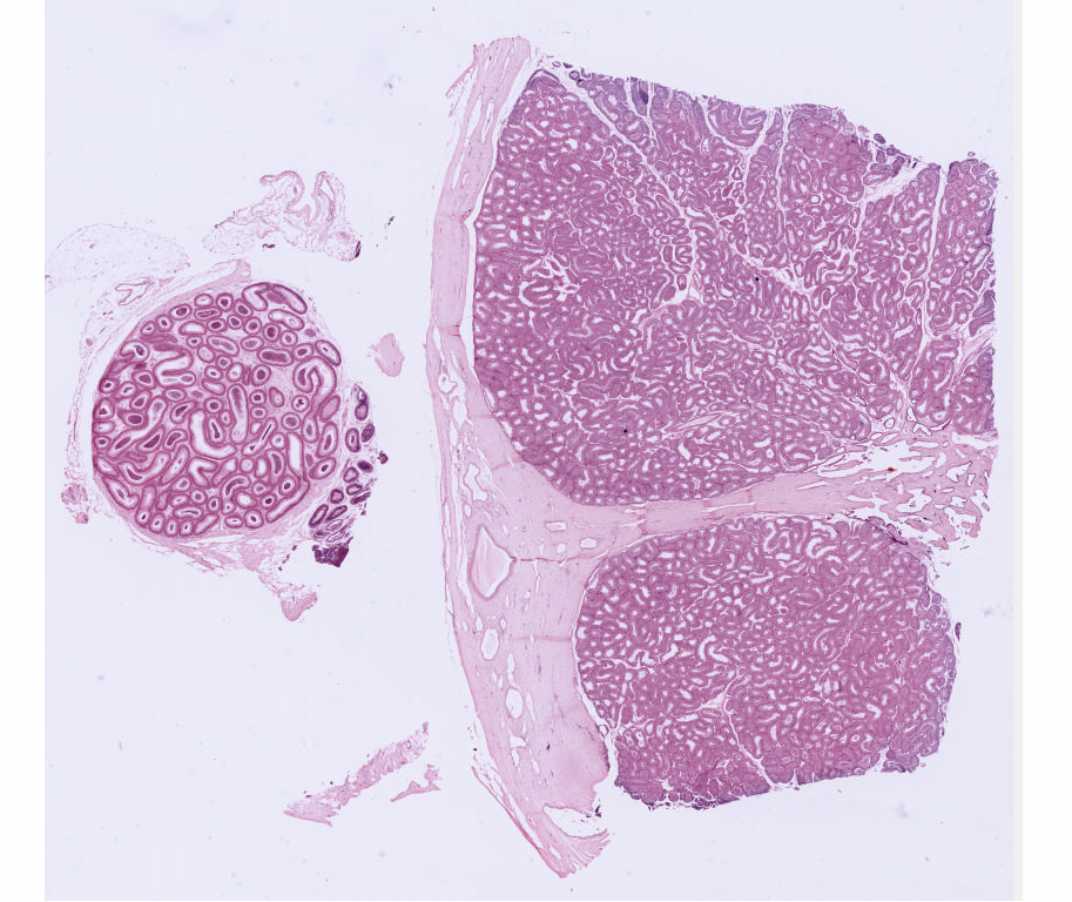
Be sure that you distinguish the sections of the testis and the epididymis on this slide.
In the portion of the slide containing the testis, examine the seminiferous tubules as in the previous slide. Find the mediastinum - the mass of acidophilic connective tissue at one pole through which the major vessels enter and leave the testis. There are portions of the ductuli recti and the rete testis in this region.
Note: for the histological characteristics of the efferent ductules consult atlases in your textbooks.
In the portion of the slide containing the epididymis note the many sections of this coiled tube with its lining of pseudostratified columnar epithelium. The cells include tall (principal) cells that have long, modified microvilli (“stereocilia”) and round basal stem cells. There is a thin coat of circular smooth muscle.
#2 Epididymis, Rat (Silver stain for Golgi) (not scanned)
The epididymis is the major site of sperm maturation and storage. The epithelial cells are absorptive and also secrete products required for maturation of sperm. The nucleus is in the basal part of the epithelial cell and is stained pinkish-red. The Golgi apparatus is stained black with silver. Note its position between the nucleus and cell apex. Note the stereocilia at the apices of the cells. Recall that they are modified microvilli and are non-motile.