The slope intercept form of a linear equation has the following form where the equation is solved for y in terms of x:
y = a + bx
b is the slope
a is a constant term. It is the y intercept, the place where the line crosses the y axis.
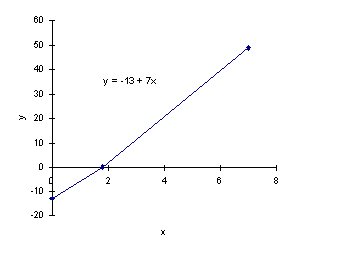
Example 1
y = -13 + 7x
This equation is in slope intercept form. The y intercept is (0,-13) and the slope is 7.

Example 2
4x + 3y = 12
Rewrite this equation in slope intercept form.
3y = 12 - 4x
The equation is now in slope intercept form. The y intercept is (0,4) and the
slope is
-4/3.
Example 3
5x - 3y - 15 = 0
Rewrite this equation in slope intercept form.
3y = -15 + 5x
The equation is now in slope intercept form. The y intercept is (0,-5) and
the slope is
5/3.
Example 4
The equation is now in slope intercept form. The y intercept is (0,-7.5) and
the slope is
1.5.
[Index]