| |
Title |
| |
|
Particulate Composite Mixing Processes
|
| |
| |
Participants |
| |
|
- Huiming Yin
- Fangliang Chen
- Lingqi Yang (Ph.D. student)
|
| |
Project Quad |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
Summary |
| |
|
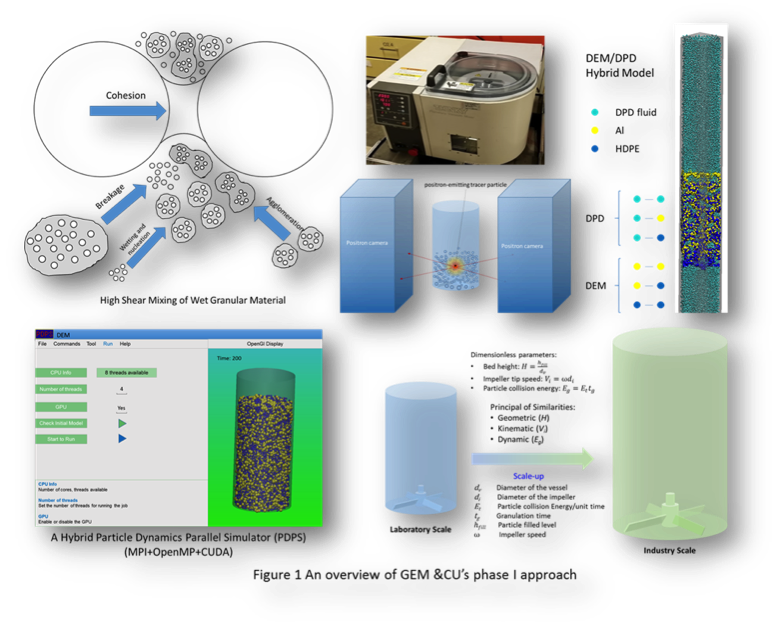
Driven by the broad industrial applications including pharmaceuticals, food, ceramics, catalysts, metals, and polymer manufacturing, the mixing of powders and granular materials has been the subject of substantial research. For those applications, it is desirable that the ingredients be mixed uniformly by strictly maintaining their concentration to meet quality and performance goals. Inefficient blending can lead to increased variability of the active component, threatening the health of patients. While considerable progress in understanding the dynamics of dry granular materials has been made recent years, the physical mechanisms underlying the properties of wet systems or in viscous fluids remain largely obscure. Although these qualitative facts are well known, a detailed knowledge of the properties has not yet been attained. Therefore, understanding mixing mechanisms and identifying critical process and material parameters is always a crucial step during process development.
|
| |
| |
|
The overall objective of the proposed work is to develop a DEM/DPD coupled granular mixing algorithms for both wet and viscous fluid operating conditions and a final software package that is able to accurately model particulate composite mixing processes in a viscous fluid in a high shear mixing environment with two or more material types of different shape, size, density, or surface roughness to a mechanically stable and homogeneous state.
|
| |
| |
|
Particle Dynamics Parallel Simulator (PDPS), which has been developed by Lingqi Yang of this group, will integrate DEM and DPD into the methodology of molecular dynamics for modeling and simulation of granular particle mixing processes. A seamless interaction of the developed solution modules with an efficient solution framework will be developed and used as a foundation for the development of a reduced order model.
|
| |
| |
Method |
| |
|
- Literature review
- Dissipative particle dynamics (DPD) for simulating interaction between liquid-liquid and solid-liquid particles
- Discrete element method (DEM) for simulating interaction between solid-solid particles
- Coupled DPD/DEM
- Experimental validation of the numerical model
|
| |
Result |
| |
|
- Empirical equations have been proposed for calibrating DPD force parameters between solid-liquid particles.
- DEM feature has been added to our software PDPS.
|
| |
| |
Publication |
| |
|
- Parametric Study in Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation toward Particle Sedimentation, 2014, Phy. Review E., under review
|
| |

