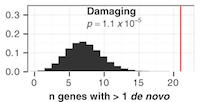
Abstract
Congenital heart disease (CHD) patients have an increased prevalence of extracardiac congenital anomalies (CAs) and risk of neurodevelopmental disabilities (NDDs). Exome sequencing of 1213 CHD parent-offspring trios identified an excess of protein-damaging de novo mutations, especially in genes highly expressed in the developing heart and brain. These mutations accounted for 20% of patients with CHD, NDD, and CA but only 2% of patients with isolated CHD. Mutations altered genes involved in morphogenesis, chromatin modification, and transcriptional regulation, including multiple mutations in RBFOX2, a regulator of mRNA splicing. Genes mutated in other cohorts examined for NDD were enriched in CHD cases, particularly those with coexisting NDD. These findings reveal shared genetic contributions to CHD, NDD, and CA and provide opportunities for improved prognostic assessment and early therapeutic intervention in CHD patients.
Data sets
All supplementary tables (a zip file):
- S1: Phenotypes for each case proband, including cardiac, neurodevelopmental disorders and extra-cardiac congenital anomalies.
- S2: List of de novo Mutations in CHD case cohort.
- S3: List of de novo Mutations in Control cohort.
- S4: List of de novo probabilities for each variant class in each protein-coding gene on the Nimblegen V2 exome, adjusted for depth in Cases.
- S5: List of de novo probabilities for each variant class in each protein-coding gene on the Nimblegen V2 exome, adjusted for depth in Controls.
- S6: Functional term enrichment analysis of all Genes with Damaging (loss of function + deleterious missense) de novo mutations in all cases.
- S7: Functional term enrichment analysis of all Genes with Loss of Function de novo mutations in 860 new cases.
- S8: List of 1,563 variants (1,161 unique genes) with damaging de novo mutations from 7 independent NDD cohorts.
- S9: Functional term enrichment analysis among 69 genes with Damaging de novo mutations overlapping between CHD cases and the published NDD (P-NDD) cohort.
- S10: Percentile ranks of genes by expression in the developing mouse heart and brain.