SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Gastrointestinal System II: Micrographs
Examine the electron Micrographs so that you understand the ultrastructural equivalents of the structures you have seen under the microscope.
Plates of Hepatocytes | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
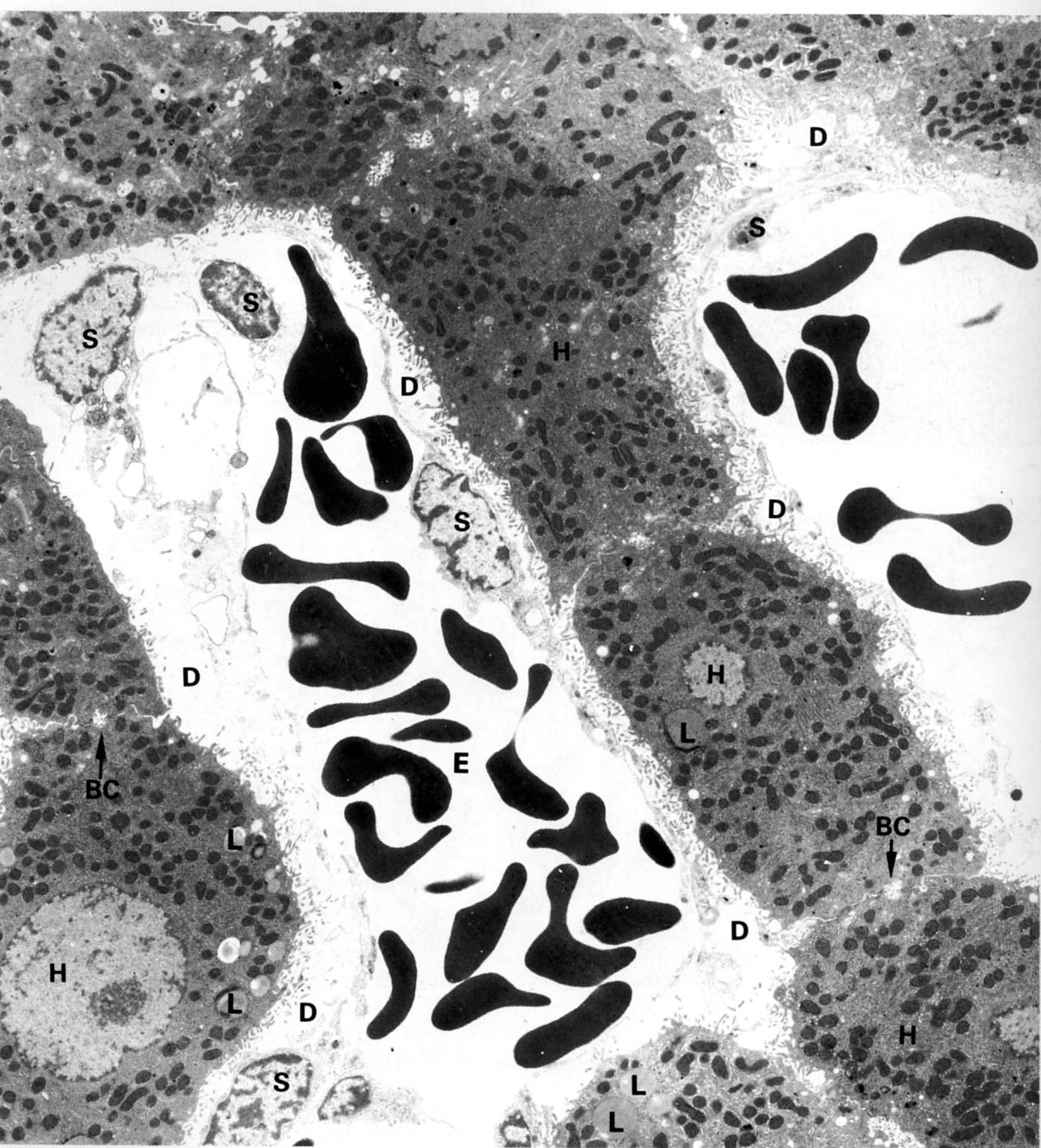 |
Plates of hepatocytes (H) border on sinusoids on two of their surfaces. Bile canaliculi (BC) are formed at adjacent hepatocytes These are sealed off by tight junctions (J). The apices of the hepatocytes are exposed to the space of Disse (D) which in turn is incompletely lined by the sinusoidal endothelium (S). The sinusoid contains whole blood (erythrocytes, E). Hepatocytes contain euchromatic nuclei and abundant, mitochondria, lipid droplets (L) and lysosomes (Ly). |
| |
Hepatocytes and Sinusoid | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
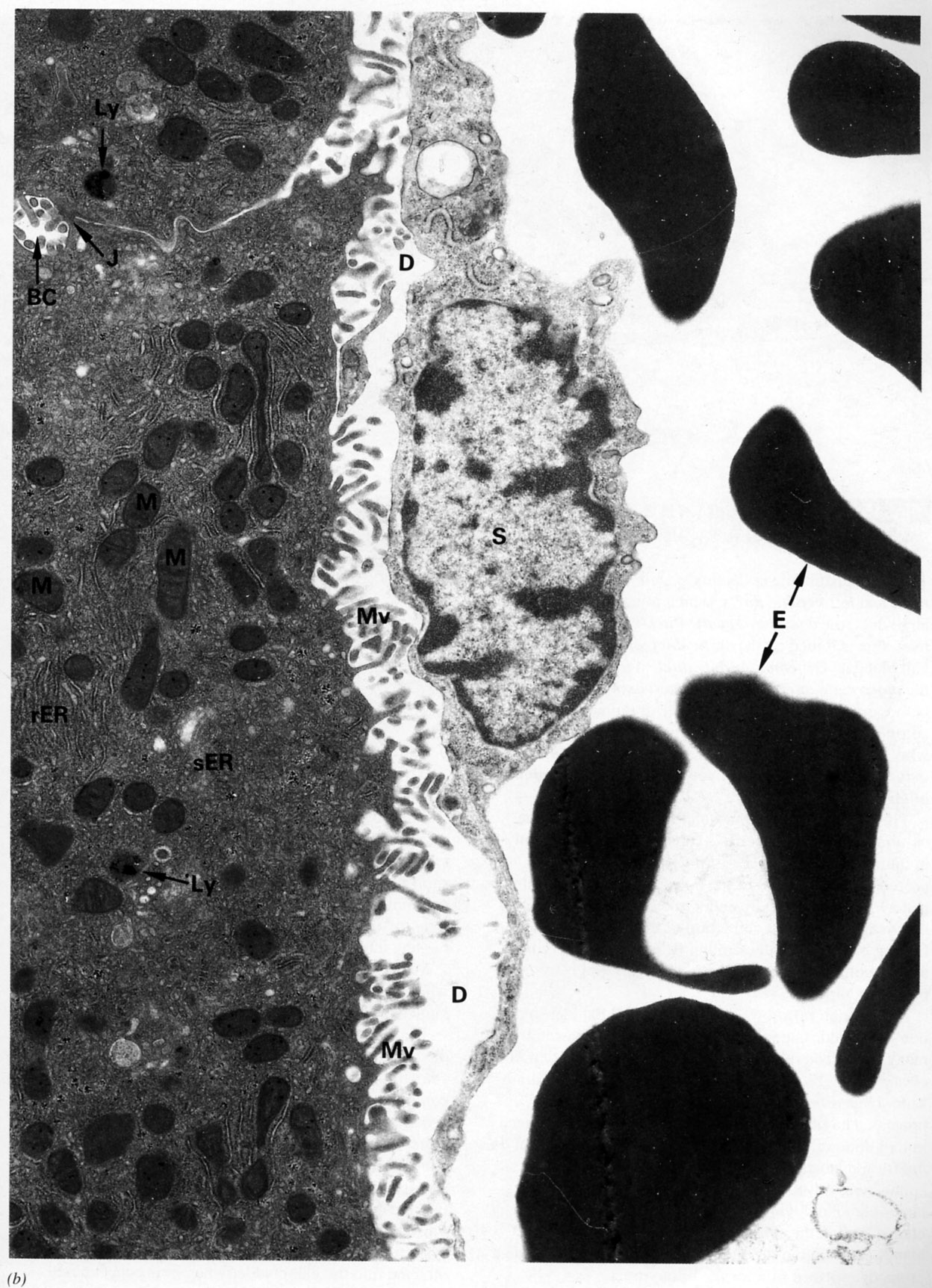 |
Hepatocytes (at left) contain abundant rER and sER and mitochondria. A bile canaliculus (BC) is formed from the plasma membranes of adjacent hepatocytes sealed off by tight junctions (J). The apex of the hepatocytes contains microvilli (Mv) and is exposed to the space of Disse (D) which in turn is incompletely lined by the sinusoidal endothelium (S). The sinusoid contains whole blood (erythrocytes, E).
|
| |
Liver Sinusoid | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
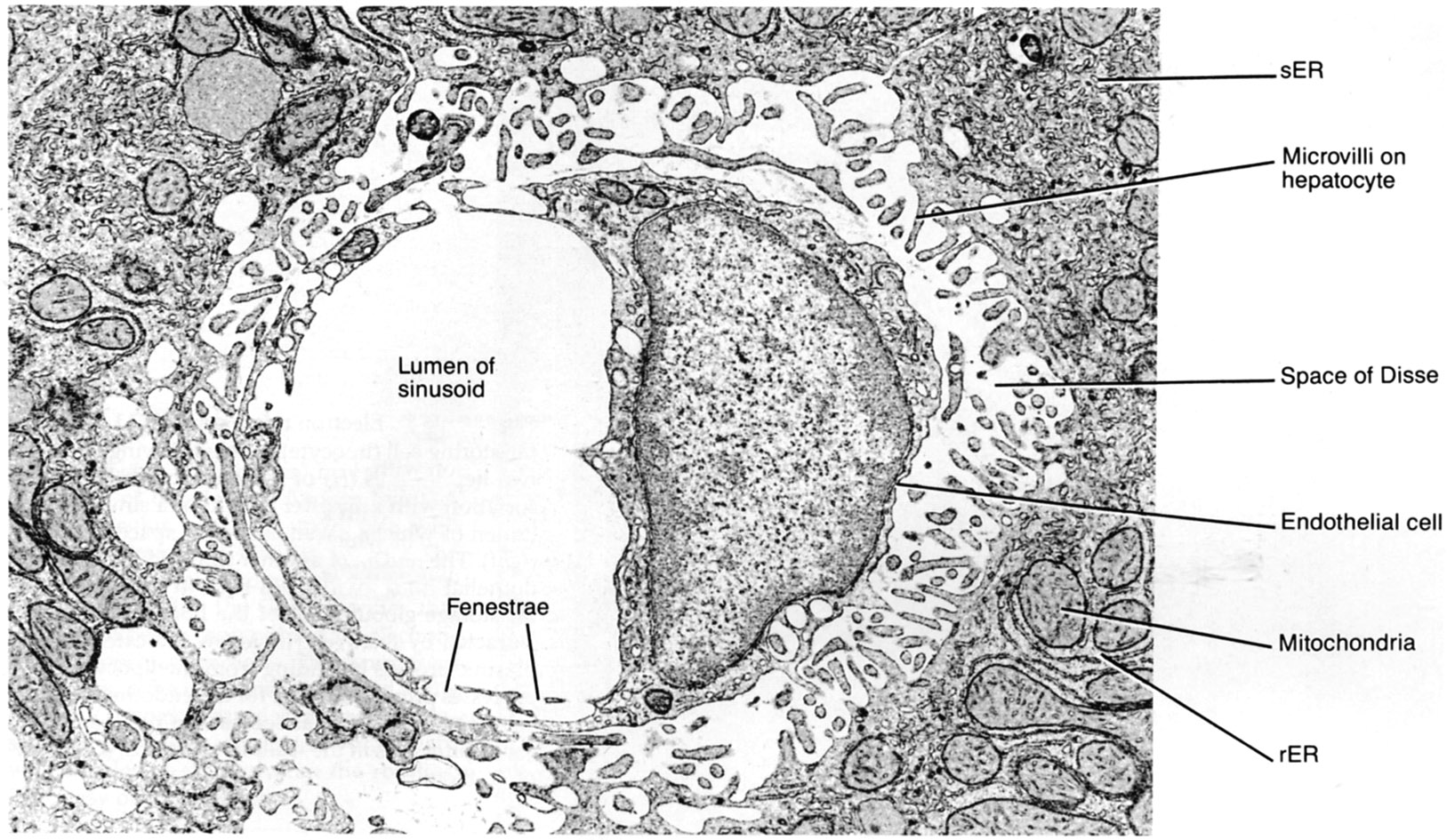 |
Liver sinusoid in cross section (rat). Open fenestrae are evident in the endothelial cell cytoplasm. Note the space of Disse between the sinusoidal wall and the hepatocytes. |
| |
Hepatic Sinusoid | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
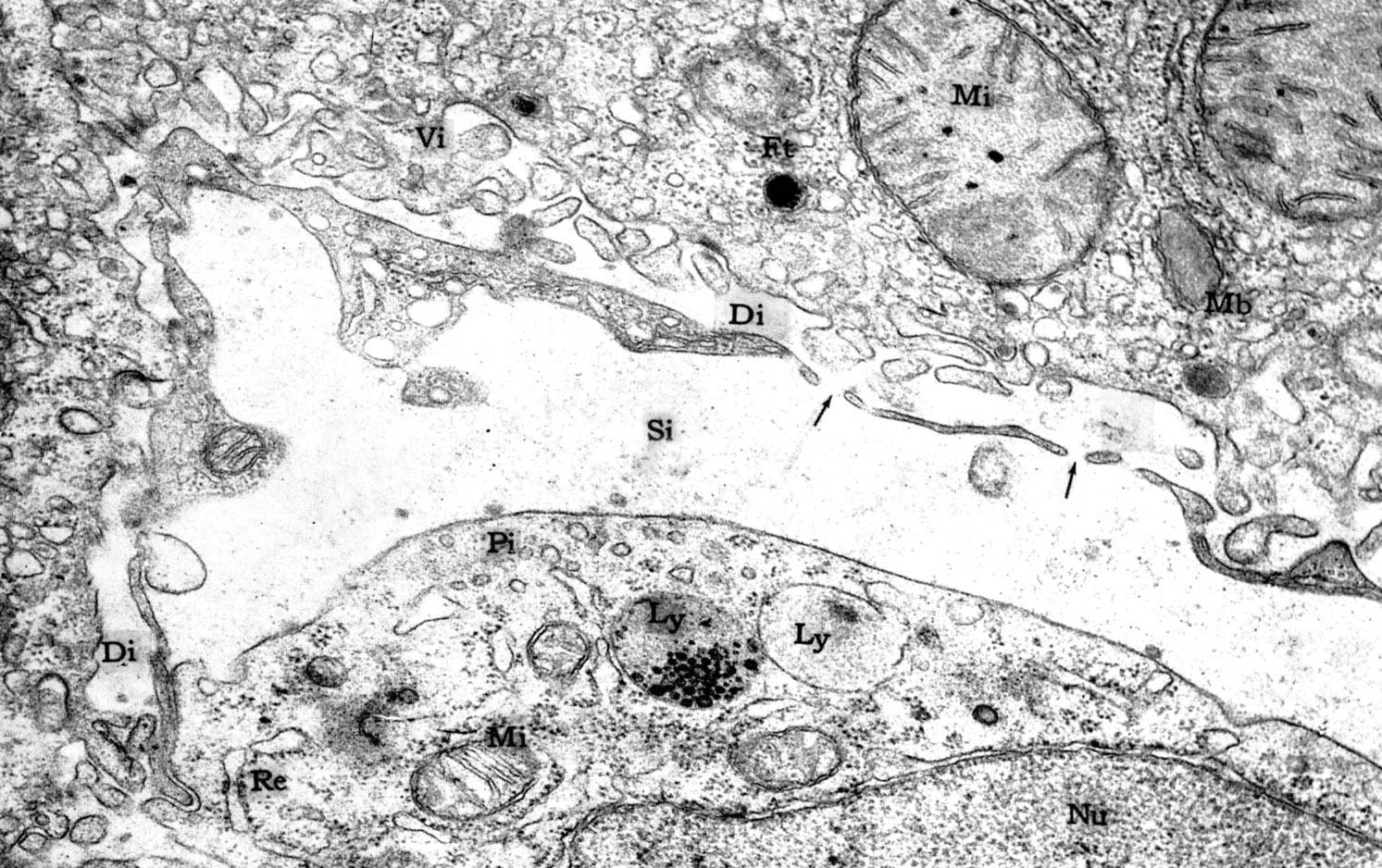 |
Sinusoids(Si) are lined by fenestrated, incomplete endothelium that defines the space of Disse (Di). Note macrophage (Kupffer cell) at the lower right with a nucleus (Nu), lysosomes (Ly), mitochondria (Mi) and endoplasmic reticulum (Re). Microvilli (Vi) of the hepatocytes extend into the space of Disse. |
| |
Liver Sinusoid - Cell | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
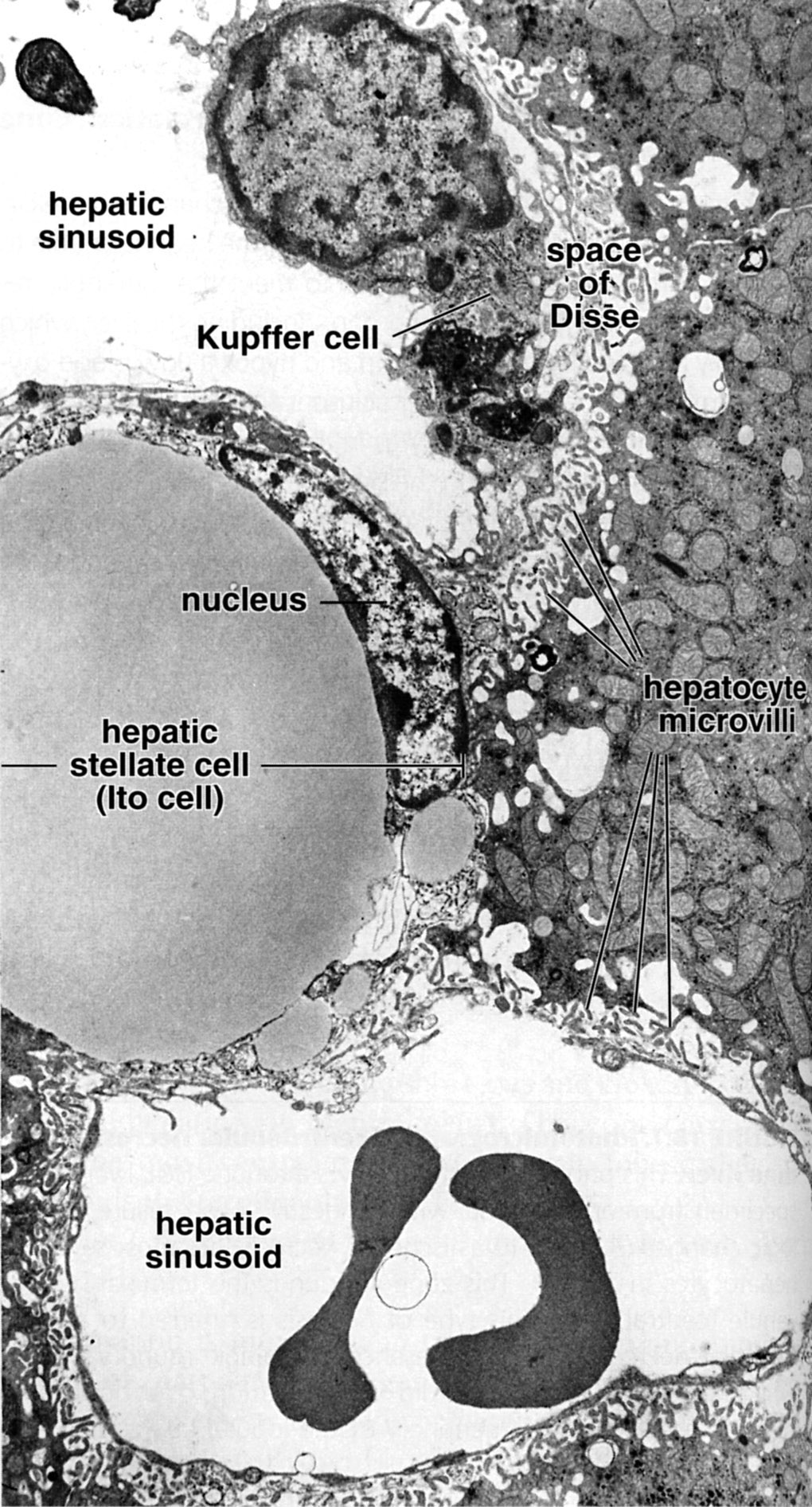 |
One hepatic sinusoid (top) displays a stellate sinusoidal macrophage (Kupffer cell). The remainder of the sinusoids is lined by highly fenestrated, discontinuous endothelium. Surrounding the sinusoid is the perisinusoidal space (space of Disse). Also present in the perisinusoidal space is an hepatic stellate cell (Ito cell) with a large lipid droplet. Its nucleus conforms to the shape of the lipid droplet. |
| |
Bile Canaliculus | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
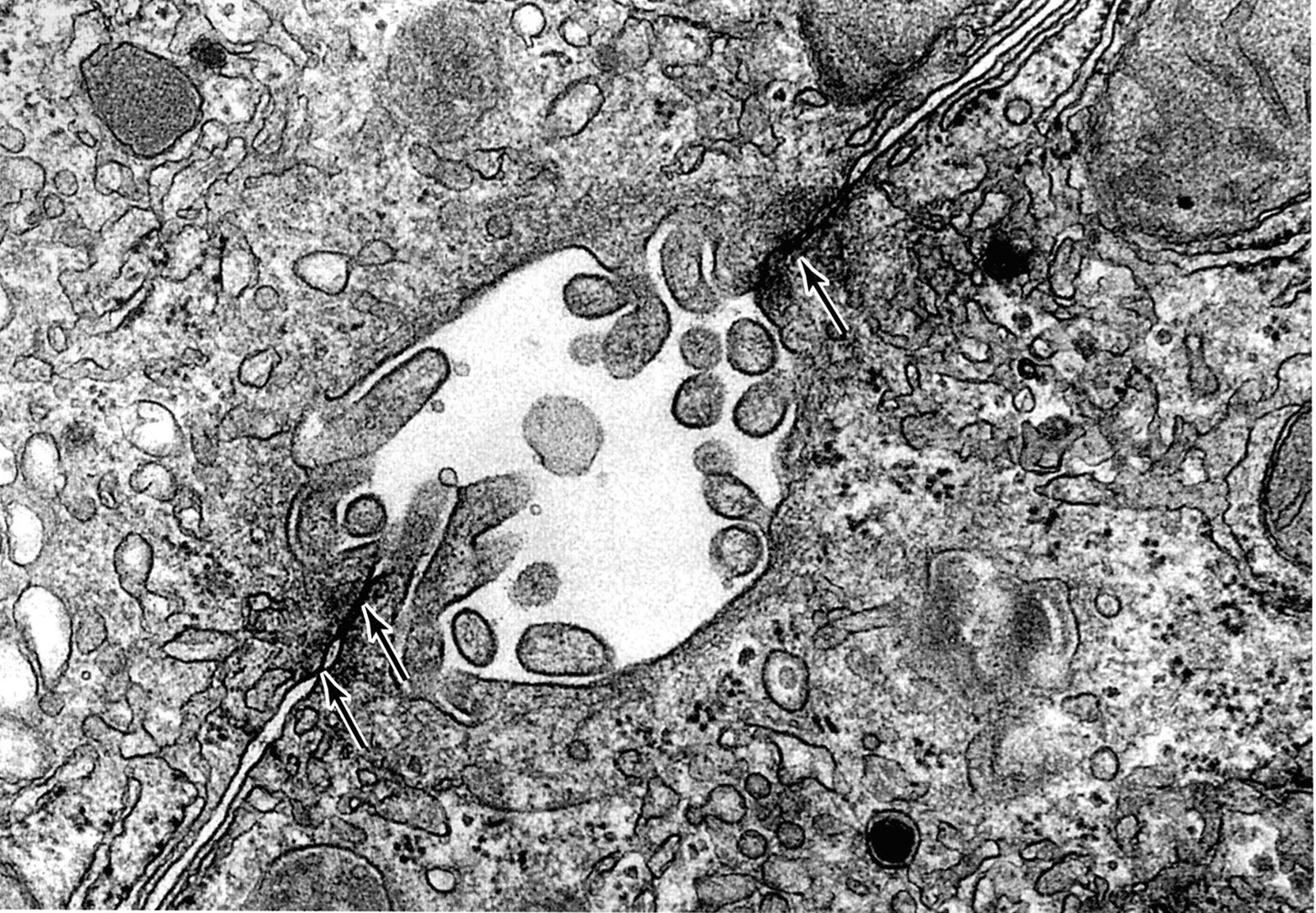 |
Junctions of two hepatocytes to form bile canaliculus (rat liver). Note microvilli in the lumen of the canaliculus and the junctional complexes (arrows) that seal off this space from the remaining extracellular space. |
| |
Pancreatic Acinar Cell | |
| Click to see enlarged view | |
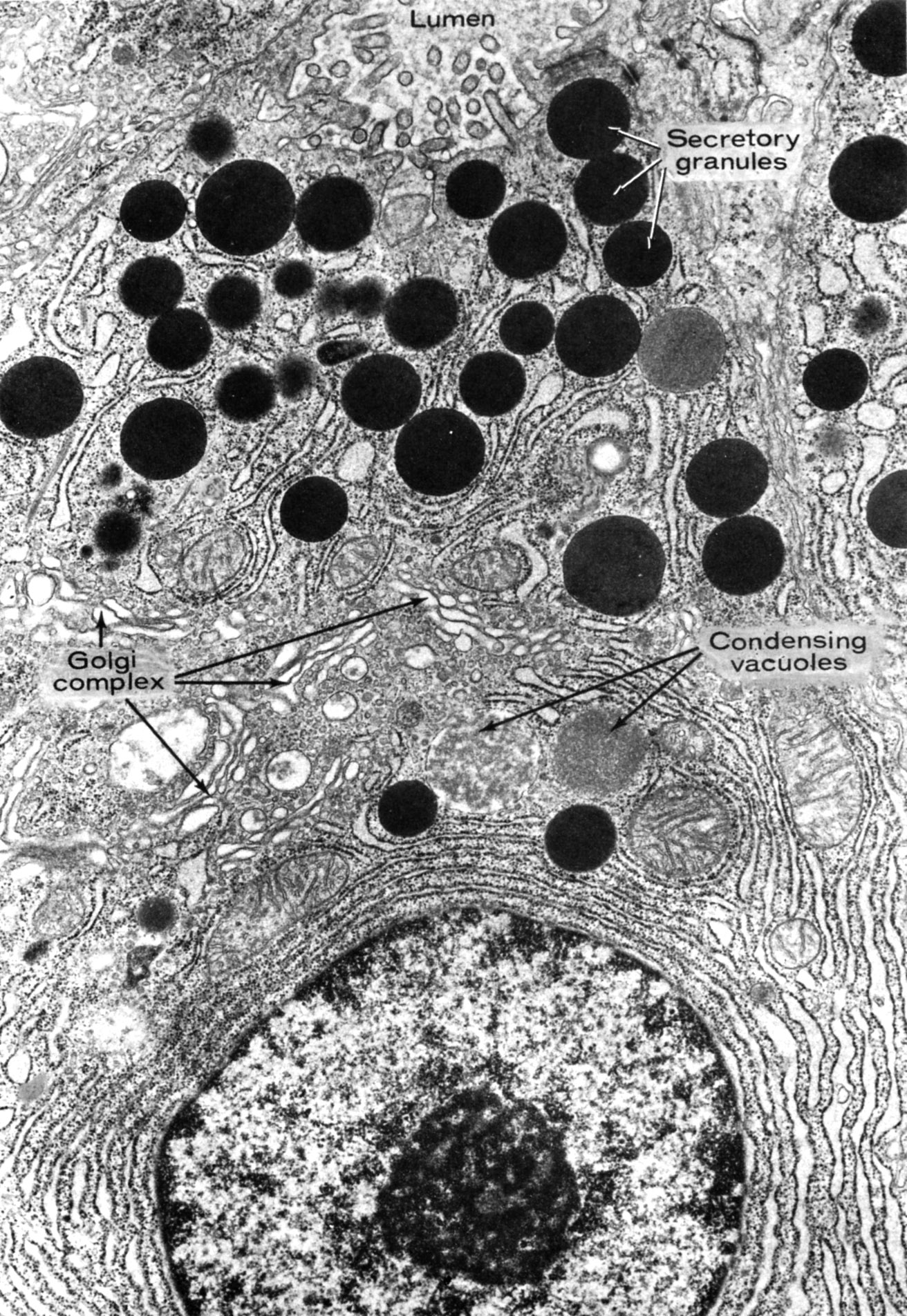 |
Supranuclear region of a pancreatic acinar cell (exocrine pancreas) illustrating condensing vacuoles in the Golgi region and mature secretory granules at the cell apex.
|